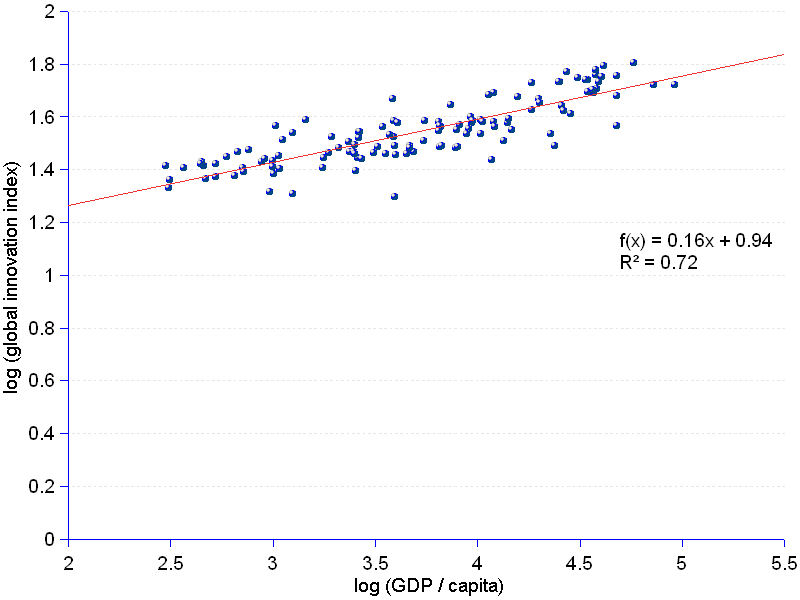
There is a clear linear association between the global innovation score and the GDP per capita for the 125 countries under consideration. The high correlation coefficient (r = 0.85) indicates a strong association. Seventy two percent of the variation of the innovation index are explained by the variation of the GDP per capita (R² = 0.72). This confirms the results of the 2009 ranking, although the sources, the methods and the panel of countries used are different.
The chart shows the logarithms of the two variables, GDP per capita on the X-axis, and the innovation score on the Y-axis. The choice of the logarithm transformation is justified by the greater simplicity of the line of fit — the red straight line —, compared to the curve that the original information would produce, and by the possibility to further understand the information behind the data by looking at the residuals.
The first evidence rendered by the chart is that high innovation indexes emerge in countries that enjoy higher GDP per capita : as the latter grows by 100 units, the innovation index climbs 16. This fact invalidates, at least partially, the popular claim that necessity is the mother of invention. In reality, you need resources to indulge into innovation — poverty is a hindrance, not a helper. However, this does not tell the full story, otherwise the data dots would coincide exactly with the straight line, which is not the case.
The analysis of residuals — a residual being the difference between the actual innovation score and the corresponding value of the line of fit — reveals that some countries endowed with comparatively high GDP per capita score low in innovation, and vice-verse. GDP per capita is not all — it explains 72% of the innovation score variation (R² = 0.72) —; some other factors must be there to explain the remaining 28%.
There is a set of countries which score higher on innovation than what their GDP per capita would entitle them to. In descending order the top ten are : China, Viet Nam, Moldova, Hong Kong, India, Sweden, Singapore, South Korea, Switzerland and Estonia. Five out of these 10 countries enjoy GDP per capita indexes that are multiples of the overall median (from 3.3 times for Korea to 10.5 for Switzerland) — they are in line with the general association between GDP and innovation. However, 5 other countries are below the median (the GDP per capita of Viet Nam is only 19% of the median, and China's is 70%). It is thus established that comparatively poor economies may succeed in achieving relatively high innovation scores. Assuming that innovation is a lever to improve economic well-being, poor countries need not lose hope — innovation is not out of reach.
At the opposite end, residuals reveal that a number of countries have an innovation performance below their GDP entitlement. The 10 lowest performers are in ascending order : Algeria, Venezuela, Brunei, Kuwait, Sudan, Greece, Yemen, Trinidad and Tobago, Syria and Kazakhstan. Six countries enjoy GDP per capita that are a multiple of the median, ranging from 1.4 times for Kazakhstan to 8.7 time for Kuwait. Four have a fraction of the median : from 17% for Yemen to 71% for Algeria. This is a mirror reflection of the situation portrayed in the last paragraph : notwithstanding enviable opportunities offered by comparatively high GDP, some countries waste their chances of attaining correct innovation indexes.
In summary, rich countries are more adept to achieve high innovation through a generous provision of education, infrastructures, administrative and political enabling environments, and financial and material support. However, The oil-rent rich countries and the largest world economies do not score impressively well. The historian Toynbee is probably right when sustaining that too much hardship crushes the ability to prosper, whilst too easy a life breeds indolence and complacency, thus preventing great achievements. Success, at least for civilizations, said Toynbee, favors those who live in a mildly hostile environment that stimulates them to reach out and accomplish prowess.
Global Innovation Index 2011 | |||||
Rank |
Country |
Score |
GDP 2010 |
Population 2011 |
GDP per capita |
| 80 | Albania | 30.45 | 10.6 | 3,269 | 3,248 |
| 125 | Algeria | 19.79 | 143.6 | 36,243 | 3,963 |
| 58 | Argentina | 35.36 | 332.2 | 41,819 | 7,944 |
| 69 | Armenia | 33 | 8.3 | 3,188 | 2,618 |
| 21 | Australia | 49.85 | 842.8 ² | 23,472 | 35,908 |
| 19 | Austria | 50.75 | 338.9 | 8,825 | 38,404 |
| 88 | Azerbaijan | 29.17 | 46.0 | 9,418 | 4,888 |
| 46 | Bahrain | 37.8 | 18.8 ² | 1,328 | 14,137 |
| 97 | Bangladesh | 28.05 | 90.2 | 151,574 | 595 |
| 24 | Belgium | 49.05 | 421.2 | 11,310 | 37,238 |
| 118 | Benin | 23.81 | 6.0 | 9,134 | 654 |
| 112 | Bolivia | 25.44 | 17.8 | 10,157 | 1,755 |
| 76 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 30.84 | 15.2 | 3,858 | 3,944 |
| 79 | Botswana | 30.51 | 13.4 | 2,041 | 6,559 |
| 47 | Brazil | 37.75 | 1,881.1 | 199,684 | 9,420 |
| 75 | Brunei Darussalam | 30.93 | 9.8 ² | 409 | 23,918 |
| 42 | Bulgaria | 38.42 | 43.0 | 7,744 | 5,551 |
| 120 | Burkina Faso | 23.14 | 7.9 | 16,998 | 468 |
| 111 | Cambodia | 25.46 | 10.2 | 14,369 | 711 |
| 103 | Cameroon | 26.95 | 20.2 | 20,122 | 1,003 |
| 8 | Canada | 56.33 | 1,418.2 | 35,722 | 39,700 |
| 38 | Chile | 38.84 | 183.3 | 17,645 | 10,388 |
| 29 | China | 46.43 | 5,296.4 | 1,366,963 | 3,875 |
| 71 | Colombia | 32.32 | 259.6 | 47,453 | 5,472 |
| 45 | Costa Rica | 37.91 | 31.1 | 4,799 | 6,489 |
| 117 | Côte d’Ivoire | 24.08 | 20.5 | 20,240 | 1,014 |
| 44 | Croatia | 37.98 | 54.8 | 4,573 | 11,990 |
| 28 | Cyprus | 46.45 | 22.8 ² | 1,146 | 19,912 |
| 27 | Czech Republic | 47.3 | 173.1 | 10,925 | 15,846 |
| 6 | Denmark | 56.96 | 279.7 | 5,804 | 48,184 |
| 93 | Ecuador | 28.75 | 53.1 | 14,861 | 3,572 |
| 87 | Egypt | 29.21 | 197.2 | 83,133 | 2,372 |
| 90 | El Salvador | 29.14 | 19.6 | 6,332 | 3,101 |
| 23 | Estonia | 49.18 | 16.8 | 1,400 | 12,017 |
| 121 | Ethiopia | 22.88 | 26.8 | 85,076 | 315 |
| 5 | Finland | 57.5 | 215.2 | 5,644 | 38,120 |
| 22 | France | 49.25 | 2,306.5 | 66,600 | 34,632 |
| 73 | Georgia | 31.87 | 10.5 | 4,473 | 2,350 |
| 12 | Germany | 54.89 | 2,981.9 | 86,457 | 34,490 |
| 70 | Ghana | 32.48 | 28.2 | 25,095 | 1,124 |
| 63 | Greece | 34.18 | 274.7 | 11,969 | 22,948 |
| 86 | Guatemala | 29.33 | 37.1 | 14,878 | 2,494 |
| 61 | Guyana | 34.83 | 2.0 | 761 | 2,629 |
| 98 | Honduras | 27.81 | 13.9 | 7,824 | 1,773 |
| 4 | Hong Kong (SAR), China | 58.8 | 202.2 | 7,387 | 27,377 |
| 25 | Hungary | 48.12 | 117.5 | 10,372 | 11,329 |
| 11 | Iceland | 55.1 | 11.3 | 336 | 33,819 |
| 62 | India | 34.52 | 1,557.8 | 1,250,232 | 1,246 |
| 99 | Indonesia | 27.78 | 636.6 | 244,191 | 2,607 |
| 95 | Iran | 28.41 | 301.7 ² | 75,579 | 3,991 |
| 13 | Ireland | 54.1 | 183.7 | 4,656 | 39,456 |
| 14 | Israel | 54.03 | 195.8 | 7,784 | 25,154 |
| 35 | Italy | 40.69 | 1,848.3 | 64,454 | 28,676 |
| 92 | Jamaica | 28.88 | 12.6 | 2,806 | 4,493 |
| 20 | Japan | 50.32 | 4,953.3 | 134,887 | 36,722 |
| 41 | Jordan | 38.43 | 24.8 | 6,363 | 3,904 |
| 84 | Kazakhstan | 30.32 | 128.8 | 16,400 | 7,855 |
| 89 | Kenya | 29.15 | 28.3 | 41,777 | 677 |
| 16 | Korea, Republic | 53.68 | 914.0 | 49,424 | 18,493 |
| 52 | Kuwait | 36.64 | 136.3 ³ | 2,827 | 48,222 |
| 85 | Kyrgyzstan | 29.79 | 4.2 | 5,444 | 764 |
| 36 | Latvia | 39.8 | 21.6 | 2,340 | 9,243 |
| 49 | Lebanon | 37.11 | 35.3 | 4,311 | 8,182 |
| 40 | Lithuania | 38.49 | 32.7 | 3,436 | 9,519 |
| 17 | Luxembourg | 52.65 | 49.6 | 536 | 92,686 |
| 67 | Macedonia | 33.47 | 8.2 | 2,109 | 3,895 |
| 113 | Madagascar | 25.41 | 7.9 | 21,414 | 367 |
| 108 | Malawi | 25.96 | 4.6 | 15,435 | 298 |
| 31 | Malaysia | 44.05 | 214.3 | 29,029 | 7,381 |
| 107 | Mali | 26.35 | 8.3 | 15,867 | 525 |
| 53 | Mauritius | 36.47 | 8.8 | 1,325 | 6,615 |
| 81 | Mexico | 30.45 | 936.7 | 116,396 | 8,047 |
| 39 | Moldova, Republic | 38.66 | 5.2 | 3,626 | 1,443 |
| 68 | Mongolia | 33.4 | 5.5 | 2,819 | 1,944 |
| 94 | Morocco | 28.73 | 82.2 | 32,545 | 2,525 |
| 78 | Namibia | 30.74 | 11.0 | 2,336 | 4,693 |
| 9 | Netherlands | 56.31 | 705.8 | 17,331 | 40,726 |
| 15 | New Zealand | 53.79 | 115.4 ² | 4,570 | 25,261 |
| 110 | Nicaragua | 25.78 | 5.9 | 5,927 | 996 |
| 122 | Niger | 21.41 | 5.0 | 16,093 | 311 |
| 96 | Nigeria | 28.15 | 174.5 | 163,115 | 1,070 |
| 18 | Norway | 52.6 | 373.4 | 5,149 | 72,519 |
| 57 | Oman | 35.51 | 42.0 ² | 2,861 | 14,690 |
| 105 | Pakistan | 26.75 | 157.5 | 177,836 | 886 |
| 77 | Panama | 30.77 | 24.1 | 3,617 | 6,670 |
| 74 | Paraguay | 31.17 | 16.6 | 6,633 | 2,509 |
| 83 | Peru | 30.34 | 138.6 | 29,739 | 4,661 |
| 91 | Philippines | 28.98 | 179.8 | 95,287 | 1,887 |
| 43 | Poland | 38.02 | 422.2 | 39,670 | 10,642 |
| 33 | Portugal | 42.4 | 205.9 | 11,198 | 18,388 |
| 26 | Qatar | 47.74 | 89.6 ² | 1,872 | 47,859 |
| 50 | Romania | 36.83 | 145.6 | 22,140 | 6,577 |
| 56 | Russian Federation | 35.85 | 1,333.3 | 147,100 | 9,064 |
| 109 | Rwanda | 25.86 | 5.1 | 10,982 | 462 |
| 54 | Saudi Arabia | 36.44 | 342.4 ² | 28,251 | 12,122 |
| 100 | Senegal | 27.56 | 11.7 | 12,786 | 913 |
| 55 | Serbia | 36.31 | 35.3 | 10,181 | 3,462 |
| 3 | Singapore | 59.64 | 200.6 | 5,285 | 37,961 |
| 37 | Slovak Republic | 39.05 | 80.2 | 5,625 | 14,261 |
| 30 | Slovenia | 45.07 | 43.0 | 2,122 | 20,277 |
| 59 | South Africa | 35.22 | 327.7 | 50,767 | 6,455 |
| 32 | Spain | 43.81 | 1,268.0 | 48,831 | 25,968 |
| 82 | Sri Lanka | 30.36 | 44.6 | 21,367 | 2,089 |
| 124 | Sudan | 20.36 | 55.9 | 44,814 | 1,247 |
| 101 | Swaziland | 27.52 | 3.3 | 1,208 | 2,718 |
| 2 | Sweden | 62.12 | 412.6 | 9,940 | 41,515 |
| 1 | Switzerland | 63.82 | 471.9 | 8,077 | 58,426 |
| 115 | Syrian Arab Republic | 24.82 | 53.2 | 20,907 | 2,547 |
| 116 | Tajikistan | 24.5 | 5.1 | 7,026 | 723 |
| 104 | Tanzania | 26.88 | 20.8 | 46,402 | 448 |
| 48 | Thailand | 37.63 | 287.3 | 70,739 | 4,061 |
| 72 | Trinidad and Tobago | 32.17 | 18.4 | 1,364 | 13,475 |
| 66 | Tunisia | 33.89 | 39.9 | 10,725 | 3,721 |
| 65 | Turkey | 34.11 | 662.4 | 74,311 | 8,915 |
| 106 | Uganda | 26.37 | 15.3 | 34,625 | 443 |
| 60 | Ukraine | 35.01 | 124.3 | 46,759 | 2,658 |
| 34 | United Arab Emirates | 41.99 | 209.8 ² | 7,896 | 26,574 |
| 10 | United Kingdom | 55.96 | 2,023.6 | 65,347 | 30,968 |
| 7 | United States | 56.57 | 13,138.2 | 325,102 | 40,413 |
| 64 | Uruguay | 34.18 | 36.3 | 3,506 | 10,349 |
| 102 | Venezuela | 27.41 | 349.4 | 29,741 | 11,749 |
| 51 | Viet Nam | 36.71 | 93.3 | 89,959 | 1,037 |
| 123 | Yemen | 20.72 | 24.0 ² | 24,877 | 966 |
| 114 | Zambia | 25.27 | 14.6 | 13,525 | 1,079 |
| 119 | Zimbabwe | 23.54 | 6.7 | 12,838 | 525 |
| Median | 34.18 | 5,551 | |||
| ¹ Converted to real $US with the GDP deflator, 2005=100. | |||||
| ² Original GDP values for 2009. | |||||
| ³ Original GDP value for 2008. | |||||
Sources: INSEAD - The Global Innovation Index for the innovation index, United Nations Population Division for population data, and World DataBank – The World Bank for GDP estimates.