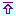

Historical build-up data of US federal budget – in real dollars, 2005=100 – suggests a strong bias for budget deficits. During the 82-year period covered here, only 14 fiscal years show a surplus, and always for a short spell, the longest being the 4-year period from 1998 to 2001, under Clinton's administration. Also surpluses are very discreet compared with deficits, in terms of percentage of total receipts. The average surplus amounts to 9.3% of total receipts (median 6.7%), whereas deficits climb to 32.3% (median 16.2%) of total receipts.
Six different behavior patterns stand out. The Wall Street crash of 1929 ushered the end of the "roaring twenties" and the beginning of the "great depression". The surpluses of fiscal years 1929 and 1930, yielded to a 16-year long period of deficits, especially large during World War II. If not in absolute terms, since the biggest deficit during the period has occurred in 2009 ($-1,288.8 billion), 1943 saw the largest deficit as a percentage of total receipts : 227.3%.
From 1946 to 1974, in spite of the Korea and Vietnam wars, spending did not diverge too much from receipts. Although only 8 fiscal years registered a surplus, deficits remained comparatively small : 1.2% to 16.5% of the annual total receipts.
From 1975 to 1997, under Ford, Carter, Reagan and G. Bush administrations, deficits increased in size (amounting to between 1.4% and 34.6% of annual receipts) and became the rule. Heavy spending in defense programs, such as "star wars", growing expenditures in social security and Medicare, and the effects of the "supply-side economics" on the receipts side (tax cuts) and on the spending side (tax expenditures), all these factors induced regular deficit budgets and the build-up of debt.
From 1998 to 2001, Clinton's "balanced budget" fiscal policies achieved new surpluses that provided G. W. Bush with a clean inheritance.
From 2002 onwards, federal budgets had a relapse. Under G. W. Bush's rule, budget deficits, and as a consequence the government debt, trended upwards under the combined effect of the costly Iraq and Afghanistan wars, the mounting pressure on spending by social security and Medicare entitlement programs, and the reactivated "voodoo economics".
Since 2009, under Obama's administration, the squeeze on tax revenues caused by the economy downturn, the swelling of spending caused by the continuation of the war, and the assets rescue, economy stimulus, social stabilizer programs launched to alleviate the impact of the financial and economic meltdown of 2008, all boosted budget deficits that, as a share of the economy, are the largest since the end of World War II.
In fact, deficits may be even larger than reported, because the government is using social security surpluses to offset other federal spending, thereby decreasing the current budget deficit, while increasing the amount of Treasury securities held by the Trust Fund.
The budget outlook, according to projections by the Congressional Budget Office, is anything but rejoicing, even under the scenario of an economy turnaround and higher tax revenues. Fiscal gaps are expected to last, causing the debt held by the public – the share of the total debt outstanding on which interest must be paid – to grow from the current level of 62% of GDP to between 66% and 87% of GDP by 2020.
Federal receipts, spending and surplus or deficit 1929-2010 | ||||||
Year |
Total receipts |
Total spending |
Surplus or Deficit (-) |
|||
| (billion current US$) | (billion real US$) ¹ | (billion current US$) | (billion real US$) ¹ | (billion current US$) | (billion real US$) ¹ | |
| 2010 | 2,161.7 | 1,953.5 | 3,455.8 | 3,122.9 | -1,294.1 | -1,169.4 |
| 2009 | 2,105.0 | 1,920.4 | 3,517.7 | 3,209.1 | -1,412.7 | -1,288.8 |
| 2008 | 2,524.0 | 2,323.7 | 2,982.5 | 2,745.8 | -458.6 | -422.2 |
| 2007 | 2,568.0 | 2,415.9 | 2,728.7 | 2,567.1 | -160.7 | -151.2 |
| 2006 | 2,406.9 | 2,331.0 | 2,655.1 | 2,571.4 | -248.2 | -240.4 |
| 2005 | 2,153.6 | 2,153.6 | 2,472.0 | 2,472.0 | -318.3 | -318.3 |
| 2004 | 1,880.1 | 1,942.9 | 2,292.8 | 2,369.3 | -412.7 | -426.5 |
| 2003 | 1,782.3 | 1,894.0 | 2,159.9 | 2,295.3 | -377.6 | -401.3 |
| 2002 | 1,853.1 | 2,011.7 | 2,010.9 | 2,183.0 | -157.8 | -171.3 |
| 2001 | 1,991.1 | 2,196.5 | 1,862.8 | 2,054.9 | 128.2 | 141.4 |
| 2000 | 2,025.2 | 2,284.6 | 1,789.0 | 2,018.1 | 236.2 | 266.5 |
| 1999 | 1,827.5 | 2,106.1 | 1,701.9 | 1,961.4 | 125.6 | 144.7 |
| 1998 | 1,721.8 | 2,013.5 | 1,652.6 | 1,932.6 | 69.2 | 80.9 |
| 1997 | 1,579.3 | 1,867.8 | 1,601.3 | 1,893.7 | -22.0 | -26.0 |
| 1996 | 1,453.1 | 1,748.8 | 1,560.5 | 1,878.2 | -107.5 | -129.3 |
| 1995 | 1,351.8 | 1,658.0 | 1,515.8 | 1,859.1 | -164.0 | -201.1 |
| 1994 | 1,258.6 | 1,575.8 | 1,461.9 | 1,830.3 | -203.3 | -254.5 |
| 1993 | 1,154.4 | 1,475.8 | 1,409.5 | 1,801.9 | -255.1 | -326.1 |
| 1992 | 1,091.3 | 1,425.9 | 1,381.7 | 1,805.3 | -290.4 | -379.4 |
| 1991 | 1,055.0 | 1,411.2 | 1,324.4 | 1,771.5 | -269.3 | -360.3 |
| 1990 | 1,032.0 | 1,429.3 | 1,253.2 | 1,735.7 | -221.2 | -306.4 |
| 1989 | 991.2 | 1,425.8 | 1,143.6 | 1,645.1 | -152.5 | -219.3 |
| 1988 | 909.3 | 1,357.4 | 1,064.5 | 1,589.0 | -155.2 | -231.6 |
| 1987 | 854.4 | 1,319.2 | 1,004.1 | 1,550.4 | -149.7 | -231.2 |
| 1986 | 769.2 | 1,222.2 | 990.4 | 1,573.7 | -221.2 | -351.5 |
| 1985 | 734.1 | 1,192.2 | 946.4 | 1,537.0 | -212.3 | -344.8 |
| 1984 | 666.5 | 1,115.2 | 851.9 | 1,425.3 | -185.4 | -310.2 |
| 1983 | 600.6 | 1,042.6 | 808.4 | 1,403.3 | -207.8 | -360.7 |
| 1982 | 617.8 | 1,114.9 | 745.7 | 1,345.8 | -128.0 | -231.0 |
| 1981 | 599.3 | 1,147.5 | 678.2 | 1,298.7 | -79.0 | -151.2 |
| 1980 | 517.1 | 1,082.9 | 590.9 | 1,237.5 | -73.8 | -154.6 |
| 1979 | 463.3 | 1,058.7 | 504.0 | 1,151.8 | -40.7 | -93.1 |
| 1978 | 399.6 | 989.0 | 458.7 | 1,135.5 | -59.2 | -146.5 |
| 1977 | 355.6 | 941.9 | 409.2 | 1,084.0 | -53.7 | -142.1 |
| 1976 | 298.1 | 839.9 | 371.8 | 1,047.6 | -73.7 | -207.8 |
| 1975 | 279.1 | 831.5 | 332.3 | 990.2 | -53.2 | -158.6 |
| 1974 | 263.2 | 858.4 | 269.4 | 878.4 | -6.1 | -20.0 |
| 1973 | 230.8 | 821.0 | 245.7 | 874.0 | -14.9 | -53.0 |
| 1972 | 207.3 | 778.4 | 230.7 | 866.1 | -23.4 | -87.8 |
| 1971 | 187.1 | 732.9 | 210.2 | 823.1 | -23.0 | -90.2 |
| 1970 | 192.8 | 792.9 | 195.6 | 804.6 | -2.8 | -11.7 |
| 1969 | 186.9 | 809.0 | 183.6 | 795.0 | 3.2 | 14.0 |
| 1968 | 153.0 | 695.0 | 178.1 | 809.3 | -25.2 | -114.3 |
| 1967 | 148.8 | 704.8 | 157.5 | 745.7 | -8.6 | -40.9 |
| 1966 | 130.8 | 638.7 | 134.5 | 656.8 | -3.7 | -18.1 |
| 1965 | 116.8 | 586.5 | 118.2 | 593.5 | -1.4 | -7.1 |
| 1964 | 112.6 | 575.6 | 118.5 | 605.9 | -5.9 | -30.2 |
| 1963 | 106.6 | 553.1 | 111.3 | 577.8 | -4.8 | -24.7 |
| 1962 | 99.7 | 522.9 | 106.8 | 560.4 | -7.1 | -37.5 |
| 1961 | 94.4 | 501.9 | 97.7 | 519.7 | -3.3 | -17.7 |
| 1960 | 92.5 | 497.4 | 92.2 | 495.8 | 0.3 | 1.6 |
| 1959 | 79.2 | 432.1 | 92.1 | 502.2 | -12.8 | -70.1 |
| 1958 | 79.6 | 439.4 | 82.4 | 454.7 | -2.8 | -15.3 |
| 1957 | 80.0 | 451.3 | 76.6 | 432.0 | 3.4 | 19.2 |
| 1956 | 74.6 | 434.8 | 70.6 | 411.8 | 3.9 | 23.0 |
| 1955 | 65.5 | 394.6 | 68.4 | 412.6 | -3.0 | -18.0 |
| 1954 | 69.7 | 427.4 | 70.9 | 434.5 | -1.2 | -7.1 |
| 1953 | 69.6 | 430.7 | 76.1 | 470.9 | -6.5 | -40.2 |
| 1952 | 66.2 | 414.4 | 67.7 | 423.9 | -1.5 | -9.5 |
| 1951 | 51.6 | 328.8 | 45.5 | 289.9 | 6.1 | 38.9 |
| 1950 | 39.4 | 269.3 | 42.6 | 290.6 | -3.1 | -21.3 |
| 1949 | 39.4 | 272.1 | 38.8 | 268.1 | 0.6 | 4.0 |
| 1948 | 41.6 | 286.3 | 29.8 | 205.1 | 11.8 | 81.3 |
| 1947 | 38.5 | 280.2 | 34.5 | 251.0 | 4.0 | 29.2 |
| 1946 | 39.3 | 316.9 | 55.2 | 445.4 | -15.9 | -128.5 |
| 1945 | 45.2 | 407.4 | 92.7 | 836.4 | -47.6 | -429.0 |
| 1944 | 43.7 | 405.1 | 91.3 | 845.6 | -47.6 | -440.4 |
| 1943 | 24.0 | 227.6 | 78.6 | 744.8 | -54.6 | -517.2 |
| 1942 | 14.6 | 146.3 | 35.1 | 351.2 | -20.5 | -204.9 |
| 1941 | 8.7 | 93.9 | 13.7 | 147.2 | -4.9 | -53.3 |
| 1940 | 6.5 | 75.3 | 9.5 | 108.9 | -2.9 | -33.6 |
| 1939 | 6.3 | 73.3 | 9.1 | 106.4 | -2.8 | -33.1 |
| 1938 | 6.8 | 77.8 | 6.8 | 78.8 | -0.1 | -1.0 |
| 1937 | 5.4 | 60.3 | 7.6 | 84.8 | -2.2 | -24.5 |
| 1936 | 3.9 | 45.8 | 8.2 | 96.1 | -4.3 | -50.2 |
| 1935 | 3.6 | 42.6 | 6.4 | 75.7 | -2.8 | -33.1 |
| 1934 | 3.0 | 35.6 | 6.5 | 78.8 | -3.6 | -43.2 |
| 1933 | 2.0 | 25.4 | 4.6 | 58.4 | -2.6 | -33.0 |
| 1932 | 1.9 | 23.8 | 4.7 | 57.6 | -2.7 | -33.8 |
| 1931 | 3.1 | 34.0 | 3.6 | 39.0 | -0.5 | -5.0 |
| 1930 | 4.1 | 39.7 | 3.3 | 32.5 | 0.7 | 7.2 |
| 1929 | 3.9 | 36.4 | 3.1 | 29.5 | 0.7 | 6.9 |
| Annual average change rate | 5.04% | 5.93% | ||||
| ¹ Current dollars deflated with the GDP deflator, 2005=100. | ||||||
Sources: US Government Printing Office, Bureau of Economic Analysis.