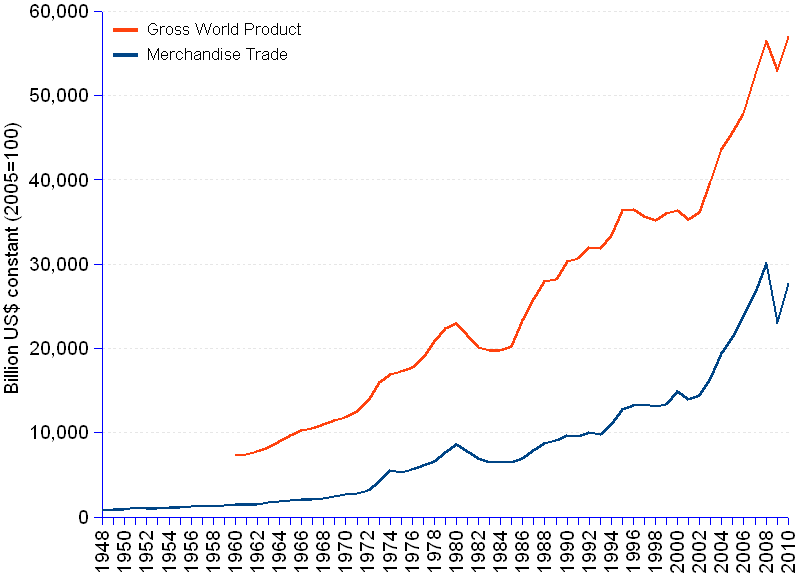
The chart shows the evolution of total merchandise trade from 1948 to 2010, and of GWP (Gross World Product) from 1960 to 2010, both in constant US dollars (2005=100). As the curves suggest, trade plays a growing role as a component of GWP. In 1960, it accounted for 19.8% of GWP, to reach 48.6% in 2010, after a peek of 53.3% in 2008, when the global crisis planted its teeth in the flesh of the world economy.
The import and export values for 1948 are evidence enough that trade has not been invented ab nihilo by the minds behind GATT (General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade), WTO (World Trade Organization), and the radical free-trade and globalization theories of the liberal school of economics. Surely, one cannot tell how would trade and GWP fare without the successive GATT Rounds of trade and tariffs negotiations, or without the Uruguay and Doha Rounds aimed at adapting the world to, and enhancing equitable participation of poorer countries in the new globalizing economy. Nevertheless, the fact remains that in 1948, in a technological, political and social context extremely remote from the situation at the dawn of the 21st century, trade was already 20% of GWP, and with or without the pull provided by the radical apostles of free-trade, it couldn't but grow in importance.
From 1960 to 2010, merchandise trade has grown faster than GWP by almost 2% annually, meaning that, at the current rates, trade would double in size 5 years faster than GWP (12 years against 17 years doubling times). But one does not know which one is the driver of the growth. We can only say that both are strongly correlated (correlation coefficient 0.98), the variation of one being mostly explained by the variation of the other (R² = 0.96).
The 2008, 2009 and 2010 bumps in both trade and GWP curves provide a revealing barometer of the storms that currently rock the world economy. The financial 2007 crisis put a subsequent halt to the world economy . In spite of the plethora of heralded rescue programs, the economy is far from being out of trouble in Q3 2011. One certainty we may learn from these events is that radical free-tradism has not been the proper medicine to rid us of the evils of the current world economy crisis.
World Merchandise Trade and Gross World Product | |||||||
Year | Merchandise exports | Merchandise imports | Total merchandise trade | Gross World Product | Trade as percent of GWP | ||
| Billion current US$ | Billion constant US$ - 2005=100 | Billion current US$ | Billion constant US$ - 2005=100 | Billion constant US$ - 2005=100 | |||
| 1948 | 58 | 400 | 62 | 427 | 827 | ||
| 1949 | 60 | 414 | 63 | 435 | 849 | ||
| 1950 | 62 | 423 | 64 | 437 | 860 | ||
| 1951 | 84 | 535 | 88 | 561 | 1,096 | ||
| 1952 | 82 | 514 | 88 | 551 | 1,065 | ||
| 1953 | 84 | 520 | 85 | 526 | 1,046 | ||
| 1954 | 87 | 533 | 89 | 546 | 1,079 | ||
| 1955 | 95 | 573 | 99 | 597 | 1,170 | ||
| 1956 | 105 | 612 | 109 | 635 | 1,247 | ||
| 1957 | 114 | 643 | 121 | 683 | 1,326 | ||
| 1958 | 110 | 607 | 115 | 635 | 1,241 | ||
| 1959 | 118 | 643 | 123 | 671 | 1,314 | ||
| 1960 | 130 | 699 | 137 | 737 | 1,436 | 7,250 | 19.8% |
| 1961 | 136 | 723 | 143 | 760 | 1,484 | 7,361 | 20.2% |
| 1962 | 143 | 750 | 151 | 792 | 1,542 | 7,765 | 19.9% |
| 1963 | 157 | 815 | 164 | 851 | 1,666 | 8,301 | 20.1% |
| 1964 | 176 | 900 | 183 | 935 | 1,835 | 8,939 | 20.5% |
| 1965 | 190 | 954 | 199 | 999 | 1,953 | 9,699 | 20.1% |
| 1966 | 208 | 1,015 | 218 | 1,064 | 2,080 | 10,234 | 20.3% |
| 1967 | 218 | 1,032 | 228 | 1,080 | 2,112 | 10,561 | 20.0% |
| 1968 | 242 | 1,099 | 252 | 1,145 | 2,244 | 10,923 | 20.5% |
| 1969 | 277 | 1,199 | 287 | 1,242 | 2,442 | 11,461 | 21.3% |
| 1970 | 317 | 1,304 | 329 | 1,353 | 2,657 | 11,839 | 22.4% |
| 1971 | 354 | 1,386 | 366 | 1,433 | 2,820 | 12,469 | 22.6% |
| 1972 | 419 | 1,573 | 433 | 1,626 | 3,199 | 13,816 | 23.2% |
| 1973 | 580 | 2,063 | 595 | 2,117 | 4,180 | 16,001 | 26.1% |
| 1974 | 840 | 2,739 | 861 | 2,808 | 5,547 | 16,943 | 32.7% |
| 1975 | 877 | 2,613 | 912 | 2,717 | 5,330 | 17,277 | 30.9% |
| 1976 | 992 | 2,795 | 1,026 | 2,891 | 5,686 | 17,778 | 32.0% |
| 1977 | 1,128 | 2,988 | 1,171 | 3,102 | 6,090 | 18,902 | 32.2% |
| 1978 | 1,307 | 3,235 | 1,358 | 3,361 | 6,597 | 20,836 | 31.7% |
| 1979 | 1,659 | 3,791 | 1,694 | 3,871 | 7,662 | 22,330 | 34.3% |
| 1980 | 2,034 | 4,260 | 2,075 | 4,345 | 8,605 | 23,003 | 37.4% |
| 1981 | 2,010 | 3,849 | 2,066 | 3,956 | 7,805 | 21,574 | 36.2% |
| 1982 | 1,883 | 3,398 | 1,941 | 3,503 | 6,901 | 20,137 | 34.3% |
| 1983 | 1,846 | 3,205 | 1,890 | 3,281 | 6,486 | 19,792 | 32.8% |
| 1984 | 1,956 | 3,273 | 2,014 | 3,370 | 6,643 | 19,803 | 33.5% |
| 1985 | 1,954 | 3,173 | 2,015 | 3,272 | 6,446 | 20,188 | 31.9% |
| 1986 | 2,138 | 3,397 | 2,206 | 3,505 | 6,902 | 23,368 | 29.5% |
| 1987 | 2,516 | 3,885 | 2,582 | 3,987 | 7,872 | 25,795 | 30.5% |
| 1988 | 2,869 | 4,283 | 2,964 | 4,425 | 8,708 | 27,901 | 31.2% |
| 1989 | 3,098 | 4,456 | 3,201 | 4,605 | 9,061 | 28,211 | 32.1% |
| 1990 | 3,449 | 4,777 | 3,550 | 4,917 | 9,694 | 30,331 | 32.0% |
| 1991 | 3,515 | 4,702 | 3,632 | 4,858 | 9,560 | 30,725 | 31.1% |
| 1992 | 3,766 | 4,921 | 3,881 | 5,071 | 9,992 | 32,034 | 31.2% |
| 1993 | 3,782 | 4,835 | 3,875 | 4,954 | 9,789 | 31,808 | 30.8% |
| 1994 | 4,326 | 5,416 | 4,428 | 5,544 | 10,960 | 33,454 | 32.8% |
| 1995 | 5,164 | 6,333 | 5,283 | 6,479 | 12,813 | 36,391 | 35.2% |
| 1996 | 5,403 | 6,503 | 5,544 | 6,672 | 13,175 | 36,440 | 36.2% |
| 1997 | 5,591 | 6,612 | 5,737 | 6,785 | 13,397 | 35,702 | 37.5% |
| 1998 | 5,501 | 6,433 | 5,681 | 6,644 | 13,077 | 35,175 | 37.2% |
| 1999 | 5,712 | 6,583 | 5,921 | 6,824 | 13,407 | 35,967 | 37.3% |
| 2000 | 6,456 | 7,283 | 6,724 | 7,585 | 14,868 | 36,336 | 40.9% |
| 2001 | 6,191 | 6,830 | 6,483 | 7,152 | 13,981 | 35,312 | 39.6% |
| 2002 | 6,492 | 7,047 | 6,742 | 7,319 | 14,366 | 36,118 | 39.8% |
| 2003 | 7,586 | 8,062 | 7,867 | 8,360 | 16,422 | 39,788 | 41.3% |
| 2004 | 9,218 | 9,526 | 9,568 | 9,887 | 19,413 | 43,598 | 44.5% |
| 2005 | 10,489 | 10,489 | 10,855 | 10,855 | 21,344 | 45,621 | 46.8% |
| 2006 | 12,113 | 11,731 | 12,437 | 12,045 | 23,776 | 47,895 | 49.6% |
| 2007 | 14,000 | 13,171 | 14,300 | 13,453 | 26,624 | 52,500 | 50.7% |
| 2008 | 16,116 | 14,837 | 16,520 | 15,209 | 30,046 | 56,397 | 53.3% |
| 2009 | 12,522 | 11,424 | 12,718 | 11,602 | 23,026 | 53,015 | 43.4% |
| 2010 | 15,238 | 13,770 | 15,376 | 13,895 | 27,665 | 56,976 | 48.6% |
| Average annual growth rate (1948-2010) | 9.4% | 5.9% | 9.3% | 5.8% | 5.8% | ||
| Average annual growth rate (1960-2010) | 10.0% | 6.1% | 9.9% | 6.1% | 6.1% | 4.2% | 1.8% |
Sources: WTO, World DataBank, and BEA.