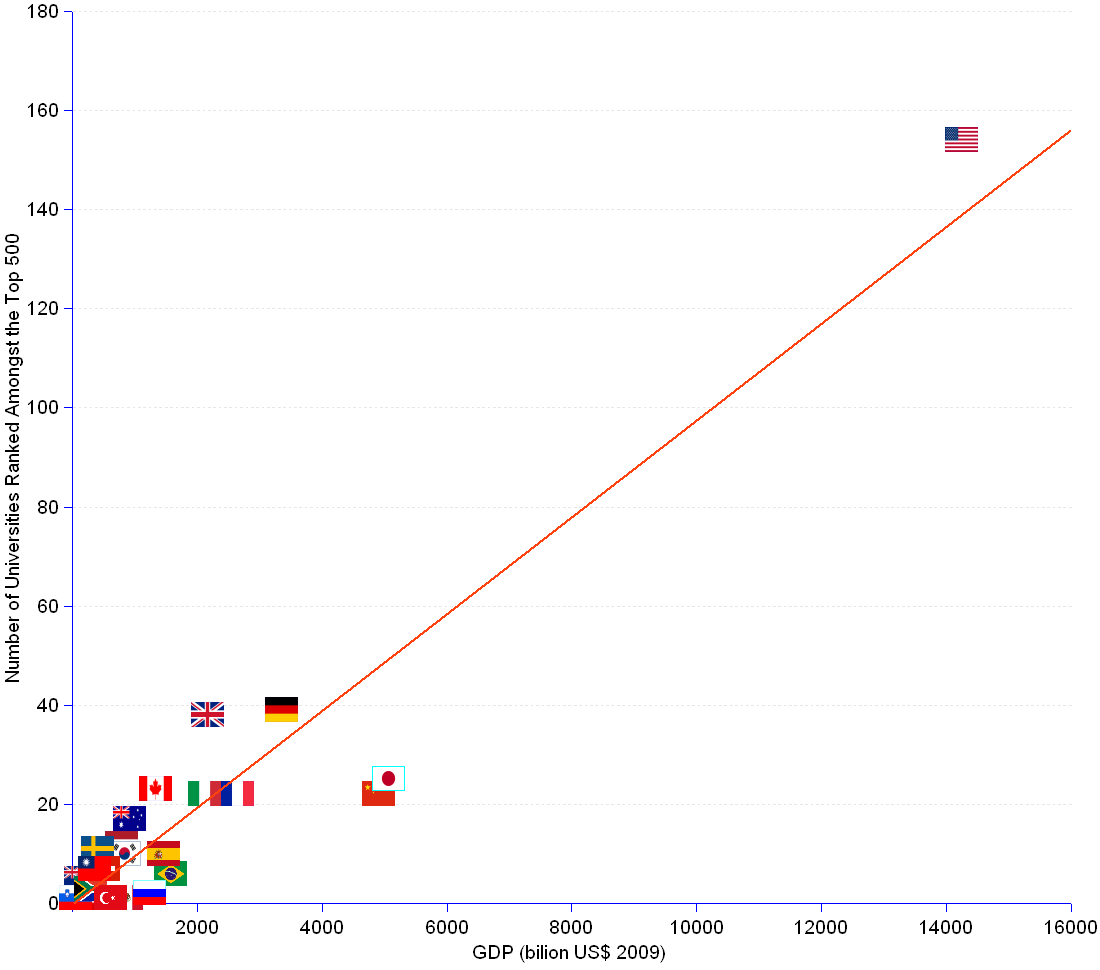
Top ranked universities are strongly correlated (R² = 0.89) with the weight of the national economy, as measured by the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The higher the GDP, the more a nation has Universities ranked amongst the top 500 worldwide. The correlation line (in red) shows that, while some nations are ahead (e.g. USA, UK, Canada) or behind the trend (e.g. Japan, China, Brazil), they all evidence the relationship between university riches and economic muscle.
Number of 500 top-ranked Universities correlated to the Gross Domestic Product | ||
Nation | Number of Universities | Gross Domestic Product |
| Argentina | 1 | 309 |
| Australia | 17 | 925 |
| Austria | 7 | 385 |
| Belgium | 7 | 469 |
| Brazil | 6 | 1572 |
| Canada | 23 | 1336 |
| Chile | 2 | 164 |
| China | 22 | 4909 |
| Czech | 1 | 190 |
| Denmark | 4 | 310 |
| Finland | 6 | 238 |
| France | 22 | 2649 |
| Germany | 39 | 3347 |
| Greece | 2 | 330 |
| Hong Kong | 5 | 215 |
| Hungary | 2 | 129 |
| India | 2 | 1296 |
| Iran | 1 | 331 |
| Ireland | 3 | 227 |
| Israel | 7 | 195 |
| Italy | 22 | 2113 |
| Japan | 25 | 5068 |
| Mexico | 1 | 875 |
| Netherlands | 12 | 792 |
| New Zealand | 5 | 125 |
| Norway | 4 | 382 |
| Poland | 2 | 430 |
| Portugal | 2 | 228 |
| Russia | 2 | 1231 |
| Saudi Arabia | 2 | 369 |
| Singapore | 2 | 182 |
| Slovenia | 1 | 48 |
| South Africa | 3 | 286 |
| South Korea | 10 | 833 |
| Spain | 10 | 1460 |
| Sweden | 11 | 406 |
| Switzerland | 7 | 500 |
| Taiwan | 7 | 362 ¹ |
| Turkey | 1 | 617 |
| United Kingdom | 38 | 2175 |
| United States | 154 | 14256 |
| Correlation coefficient R² = 0.89 | ||
| ¹ 2009 estimate, CIA World Factbook | ||
Sources: Institute of Higher Education, Shanghai, and World Development Indicators database by World Bank.